Introduction to MATLAB
 In this introduction we will describe how MATLAB handles simple numerical expressions and mathematical formulas. The name MATLAB stands for MATrix LABoratory. MATLAB was written originally to provide easy access to matrix software developed by the LINPACK (linear system package) and EISPACK (Eigen system package) projects. MATLAB is a high-performance language for technical computing. It integrates computation, visualization, and programming environment. Furthermore, MATLAB is a modern programming language environment: it has sophisticated data structures, contains built-in editing and debugging tools, and supports object-oriented programming. These factors make MATLAB an excellent tool for teaching and research.
In this introduction we will describe how MATLAB handles simple numerical expressions and mathematical formulas. The name MATLAB stands for MATrix LABoratory. MATLAB was written originally to provide easy access to matrix software developed by the LINPACK (linear system package) and EISPACK (Eigen system package) projects. MATLAB is a high-performance language for technical computing. It integrates computation, visualization, and programming environment. Furthermore, MATLAB is a modern programming language environment: it has sophisticated data structures, contains built-in editing and debugging tools, and supports object-oriented programming. These factors make MATLAB an excellent tool for teaching and research.
Key Features
High-level language for scientific and engineering computing
Desktop environment tuned for iterative exploration, design, and problem-solving
Graphics for visualizing data and tools for creating custom plots
Apps for curve fitting, data classification, signal analysis, control system tuning, and many other tasks
Add-on toolboxes for a wide range of engineering and scientific applications
Tools for building applications with custom user interfaces
Interfaces to C/C++, Java, .NET, Python, SQL, Hadoop, and Microsoft Excel
Royalty-free deployment options for sharing MATLAB programs with end users
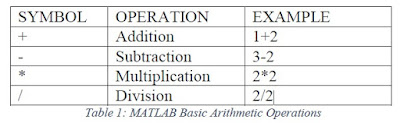
MATLAB - Basic arithmetic operations
MATLAB – Variables
Variable names are case sensitive. Variable names must start with a letter and can be followed by letters, digits and underscores.
MATLAB – Relational Operators
MATLAB supports six relational operators
MATLAB – Logical Operators
MATLAB supports three logical operators
Writer: H.L.C Fernando.










No comments:
Post a Comment